Entering the world of tree measurement is more than a technical exercise; it’s a journey into the heart of the natural world. Trees, often referred to as the silent giants of our landscapes, have stories written in every ring and branch. By learning how to measure a tree’s diameter, we open a window into its age, health, and ecological role. This simple act becomes a meaningful way to connect with the living history rooted in our backyards, parks, and forests.
Measuring a tree’s diameter isn’t just for foresters or arborists; it’s a valuable skill for homeowners, gardeners, educators, and anyone with a curiosity about the natural world. Whether you're managing tree health, planning a garden, or conducting a tree inventory, understanding a tree’s dimensions can guide informed decisions and spark deeper appreciation.
The Significance of Tree Diameter
Before we dive into the practical steps on how to measure a tree’s diameter, it’s important to understand why this simple measurement is so valuable. Measuring tree diameter at breast height (DBH) is more than just collecting numbers; it provides critical insights into a tree’s age, growth rate, health, and environmental benefits. Whether you're a tree care professional, a landscape designer, a forestry expert, or a homeowner passionate about trees, knowing how to measure a tree can help you make informed decisions about maintenance, planting, or even relocation.
Tree diameter plays a key role in assessing a tree’s contribution to carbon sequestration, its ability to provide shade, and its overall impact on the ecosystem. It also helps determine the structural integrity and long-term viability of the tree. From tree inventory management to environmental conservation, measuring a tree's diameter connects us more deeply with the natural world and supports sustainable land and forest management. By understanding this essential metric, we not only promote better tree health but also foster a stronger connection to the green spaces that surround us.
How to Measure Single Trunk Trees on Level Ground
Measuring single-trunk trees on level ground, especially for assessing diameter at breast height (DBH) can be done using a straightforward process.
Tools: Measuring Tape or Caliper Rule, Marker (Pencil, thumbtack, etc.), String
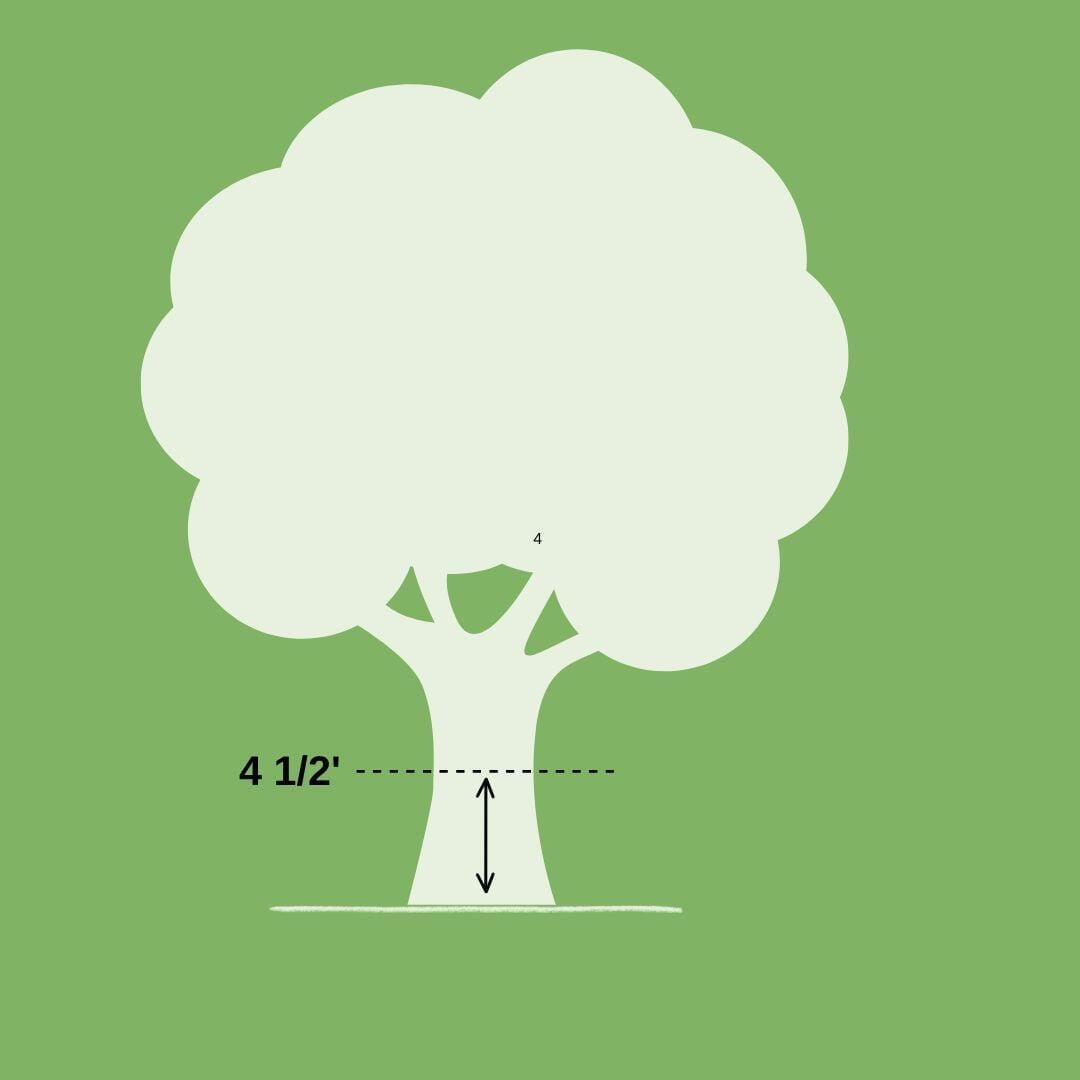

1. With the measuring tape, measure 4.5 feet up the trunk of the tree from the ground. Use a thumbtack to mark the height on the tree.
2.Wrap your string around the tree trunk at 4.5 feet. Make sure the string is straight and tight around the trunk, and mark or cut the circumference on the string.
3. Measure the length of string to get the circumference of the tree.
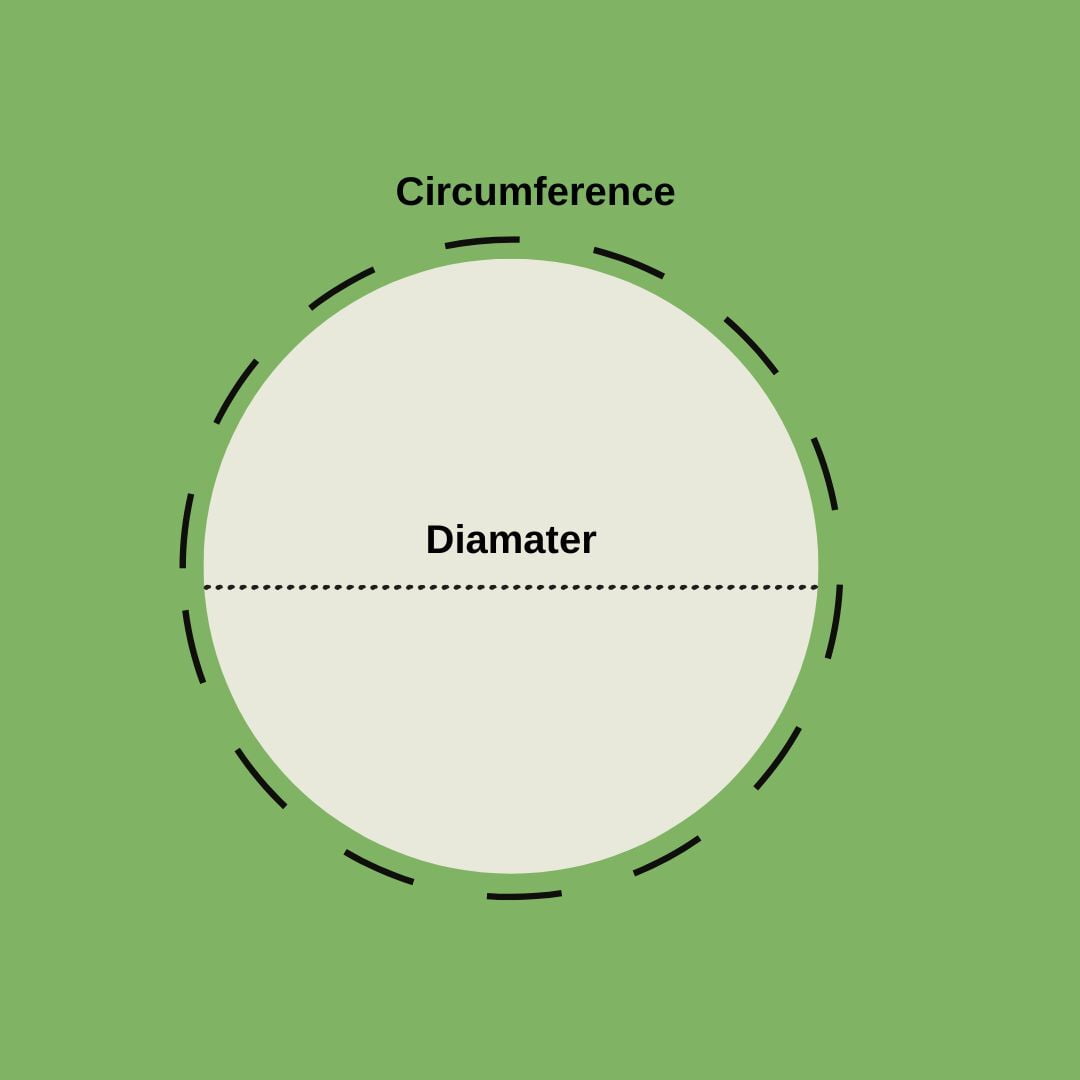
4. Convert the circumference measurement to diameter by dividing the circumference by pi (3.14)
Measuring Trees at an Angle or On a Slope
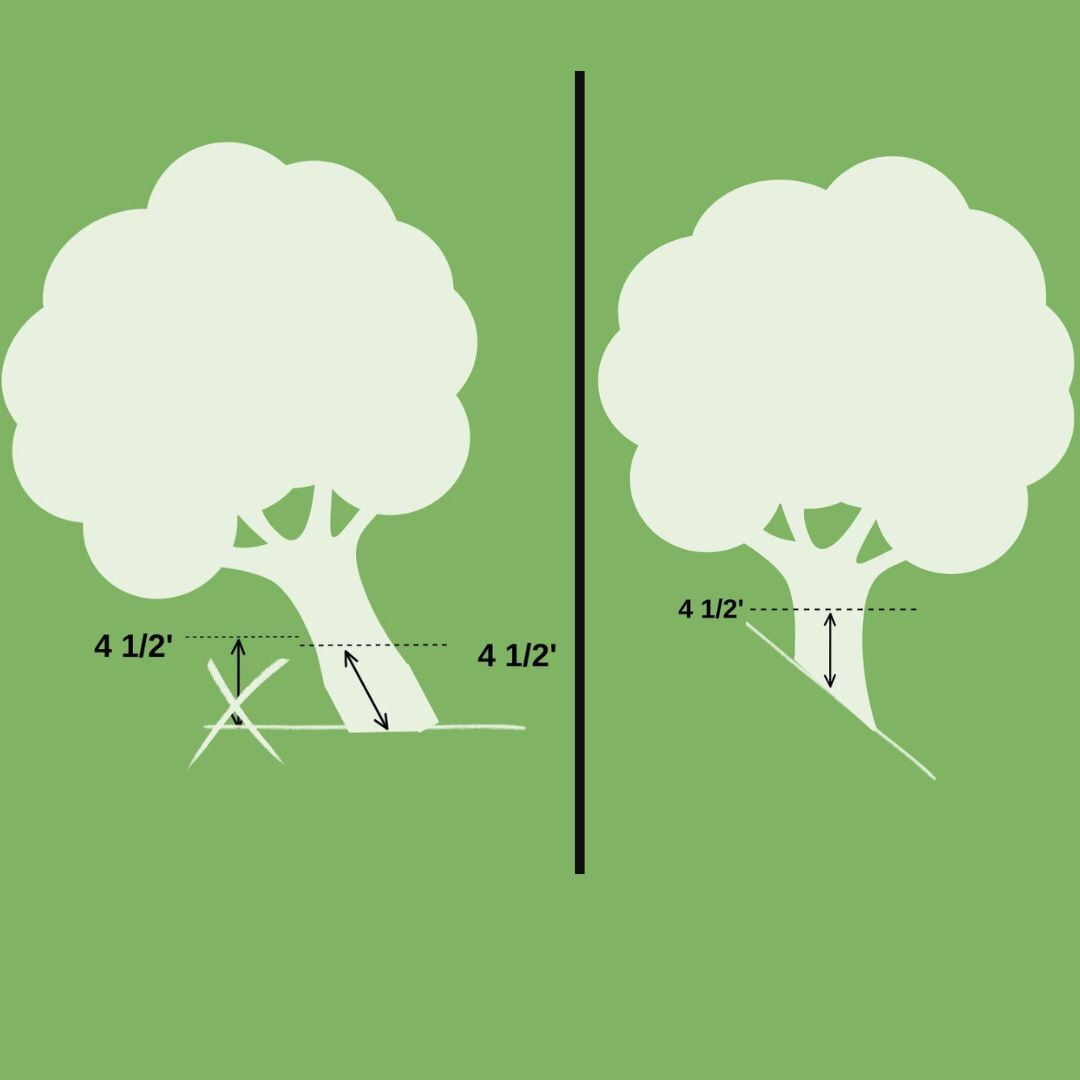
1. Select Measurement Height
Choose the standard measurement height, typically at breast height (4.5 feet or 1/37 meters above ground level). This height provides standardized tree diameter measurements.
2. Level the Measuring Point
Use a level to find a point on the tree trunk that is perpendicular to the ground at the chosen height. If the tree is on a slope, find a reference point that is level with the slope, or use a leveling instrument to identify a level point.
3. Position the Measuring Tape or Caliper Rule
Wrap the measuring tape or caliper rule around the tree trunk at the selected height, ensuring it is level. If using a caliper rule, close it gently until it touches the tree trunk.
4. Account for Slope
If measuring on a slope, use an inclinometer to measure the slope angle. Adjust your measurement to account for the slope and ensure accuracy.
5. Read the measurement
Read the measurement on the tape or caliper rule. Record the measurement in inches or centimeters.
6. Repeat for Accuracy
Take multiple measurements around the tree trunk at the selected height, especially if the trunk is irregularly shaped. This helps ensure accuracy in your average diameter.
7. Mark the measurement point
If you need to return to the same measurement point later, mark it with a pencil or marker. This is useful for monitoring the tree's growth over time.
Measuring Trees with a Split Trunk
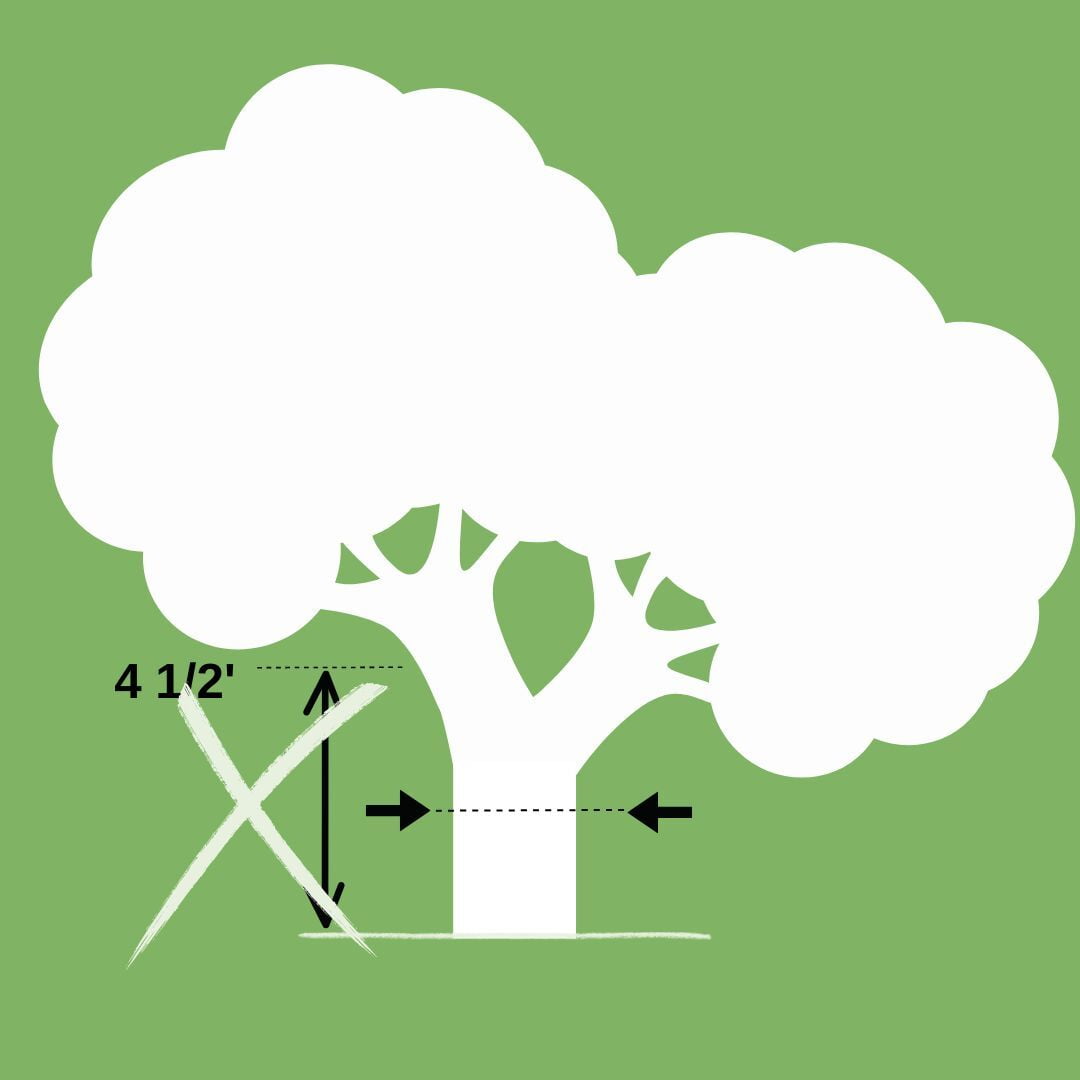
1. Identify the Measurement Point
Locate the standardized height for measurement, typically referred to as breast height. This is usually 4.5 feet (1.37 meters) above the ground.
If the split of the trunk occurs below this height, choose a point above the split where the trunk is more consolidated.
2. Wrap the Tape
Use a measuring tape or a diameter tape deigned for tree measurement.
For a split trunk, wrap the tape around the consolidated part above the split. Ensure it is level and snug, following the contour of the tree.
3. Record the Measurement
Note the measurement from the tape. If using a diameter tape, it may directly provide the diameter reading.
4. Adjust for the Split
If the split in the trunk is significant and affects the accuracy of your measurement, consider taking separate measurements for each segment of the split trunk.
Add the individual measurements together to get the total diameter of the tree. This accounts for the space between the split portions.
5. Repeat if Necessary
For irregularly shaped split trunks, consider taking multiple measurements at different points above the split to capture the tree’s overall diameter accurately.
6. Calculate Circumference and Volume.
If you’re interested in more comprehensive data, use the measured diameter to calculate the tree’s circumference (C = pi(3.14) * D ) and estimate its volume.
7. Document and Verify
Record the measurement carefully, noting any observations about the split trunk. If possible, verify your measurements with additional assessments to ensure accuracy.
Remember, the goal is to measure the consolidated part of the trunk above the split while accounting for the unique characteristics of the tree. Adapt your approach based on the specifics of the split and aim for a measurement that accurately represents the tree’s overall diameter.
Why Tree Movers Need To Know The Diameter of a Tree prior to Relocation
Equipment and Logistics Planning
The diameter of a tree determines the size of the root ball that needs to be prepared for relocation. Knowing the diameter helps tree movers choose the appropriate equipment and plan logistics for a successful move.
Root Ball Size Calculation
The diameter is directly related to the size of the root ball that needs to be excavated and preserved during the relocation process. This ensures the tree's root system remains intact, promoting its survival in the new location.
Transportation Considerations
The diameter of a tree influences the transportation process. It helps determine the space required for moving the tree, whether it's within a property or for longer distances on the road.
Site Preparation
Knowledge of the tree's diameter is essential for proper site preparation at the destination. It allows tree movers to ensure that the new location is suitable for the tree's size and accommodates its growth.
Safety and Precision
Accurate measurements of the tree's diameter contribute to the overall safety and success of the relocation. It helps tree movers plan the process with precision, minimizing the risk of damage to the tree during the move.
Cost Estimation
The diameter of a tree influences the overall cost of relocation. Larger trees with wider diameters may require more labor, equipment, and resources, impacting the overall budget for the tree-moving service.
Environmental Considerations
Understanding the diameter helps tree movers assess the environmental impact of the relocation. It allows for careful planning to minimize stress on the tree, ensuring its successful adaptation in the new environment.
In summary, knowing the diameter of a tree is crucial for tree movers to plan and execute a successful relocation process. It enables them to make informed decisions, ensure the tree's health and safety, and provide accurate estimates to their clients.
